Device Management
Apple Device Management Glossary

In this guide we will help you understand the various acronyms and terminology used in the Apple device management ecosystem.
As some terminology is changing or has already been modified by Apple, you may find different generations of acronyms in the technical documentation of different MDM vendors. This guide will try to clear this up by pointing out what legacy terminology is known as today.
- MDM (Mobile Device Management)
- Apple Configurator
- iMazing Configurator
- iMazing Profile Editor
- Apple Business Manager (ABM)
- Apple School Manager (ASM)
- Apple Business Essentials (ABE)
- Automated Device Enrollment (ADE)
- Supervision
- Apps and Books
- Apple Developer Program
- Apple Enterprise Developer Program
- Custom Enterprise App
- Configuration Profile (.mobileconfig)
- Provisioning Profile (.mobileprovision)
- Managed Apple Accounts
- Apple Account (standard)
- User Enrollment (BYOD)
- Device Enrollment
- Organization / Supervising Identity / Supervising Host Certificate
- Blueprint
- Certificate
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
- Device Management / Remote Management
- Volume Purchase
- Volume Purchase Program (VPP)
- Device Enrollment Program (DEP)
- Student Information System (SIS)
- macOS Server
- Preference File Manifest (PFM)
- Property list files (.plist)
- Trust Anchor Certificate
- Multi Factor Authentication (MFA or 2FA for two-factor authentication)
- Apple Deployment Programs (ADP)
- Apple Push Notification Service (APNs)
- App Redemption Code
- D-U-N-S Number (Data Universal Numbering System)
- Volume Purchase Token (VPP Token or sToken)
- Managed Apps
- Managed Books
- Single App Mode
- Mobile Application Management (MAM)
MDM (Mobile Device Management)
Mobile Device Management (MDM) is a system used by organizations to manage fleets of computers and devices remotely, without the need to have physical access to them. More specifically, MDM solutions allow managing provisioning, deployment and security of devices used by an organization. It encompasses various aspects including setup, configuration, policy implementation, authentication methods, and app licensing and distribution, among others.
In other words, MDM allows IT teams to provide employees with devices that are "ready for use" – saving employees time on configuration of their assigned devices and giving organizations control on what their devices and users can do.
In Apple's ecosystem, MDM applies not only to mobile devices but also to computers (so both Mac laptops and desktops as well as iPhone, iPad and Apple TV devices). For historical reasons it retains the 'mobile' moniker but is taken to simply mean 'remote' management of devices.
Apple has long been offering a vast protocol for third parties to build both internal and commercial MDM services upon, and has recently started offering its own MDM service known as Apple Business Essentials.
For more information please visit the MDM section of our Understanding Supervision, MDM, ADE (DEP), and Volume Purchase (VPP) guide.
- Wikipedia: Mobile device management
Apple Configurator
Apple Configurator is the name of two device configuration applications developed by Apple, one runs on macOS and the other on iOS.
Apple Configurator for macOS (formerly known as Apple Configurator 2 - AC2) is available for free on the Mac App Store. It allows editing and installing configuration profiles, installing apps, supervising and can automatically enroll devices in an MDM solution locally. It also allows applying blueprints (template of configurations) to iOS, iPadOS, and tvOS devices to easily configure devices in bulk.
The app was originally launched in 2012 at version 1.0. Later with version 2.0 the app was renamed Apple Configurator 2 to hail major changes that came with that version as well to mark a departure from its predecessor, iPhone Configuration Utility. In 2021 however, the app was renamed back to Apple Configurator with version 2.15.1.
In 2021, Apple launched Apple Configurator for iOS, which is available for free on the App Store. This app is specifically meant for helping IT administrators register iPhone and iPad devices, as well as Mac computers with Apple Silicon or with an Apple T2 Security Chip, in ABM and ASM.
For more information please visit the Apple Configurator page.
iMazing Configurator
iMazing Configurator is a set of tools designed to help administrators configure and provision Apple mobile devices locally, as well as automate backup/erase/update tasks. Like Apple Configurator it can supervise and enroll devices in an MDM solution as well as install volume-purchased apps, and it offers creating, editing and applying blueprints to a large number of devices simultaneously.
It was developed in response to growing requests from our enterprise customers for a solution that could handle preparing and configuring both company and BYOD iOS devices whilst being mindful of the data they may contain. Compared to Apple Configurator, it also offers more control and advanced options for local provisioning and deployment of fleets of iOS, iPadOS and Apple TV devices.
iMazing Configurator is packaged within the macOS version of our iOS data management app iMazing. There is no separate download – the feature is unlocked via activation of iMazing with an iMazing Configurator Edition license code.
For more information please visit the iMazing Configurator product page.
iMazing Profile Editor
iMazing Profile Editor (IPE) is an application that allows you to create, edit, and sign Apple configuration profiles. It is designed to easily define settings, ready to be deployed locally or via MDM on fleets of iPhones, iPads, Macs and other Apple devices.
A convenient and intuitive user interface generates standards-compliant configuration profiles, eliminating the need to manually code XML files.
Configuration profiles generated with iMazing Profile Editor are compatible with Apple devices and any compliant software or service, including MDM services that support profiles. iMazing Profile Editor also supports export of configured payloads for MDM services that only accept domain-specific Plist files.
iMazing Profile Editor is available both with iMazing as an embedded app and as stand-alone download. It can work in conjunction with iMazing Configurator.
For more information please visit the iMazing Profile Editor product page.
Apple Business Manager (ABM)
Apple Business Manager is a web portal for IT administrators that works in conjunction with third-party mobile device management (MDM) solutions.
It allows organizations to automatically supervise and enroll devices in MDM, and make volume purchases of apps as well as books for assignment in MDM.
In order for devices to be eligible for automatic supervision and MDM enrollment (a technology known as Automated Device Enrollment – ADE), they need to be added to ABM. This can be done after purchase using Apple Configurator (Add devices from Apple Configurator to Apple Business Manager), however devices purchased through Apple, an authorized reseller, or a cellular carrier can be added before shipping.
Finally, ABM allows IT administrators to create and manage the organization's Managed Apple Accounts, which are necessary in some corporate environments where employees cannot use personal Apple Accounts.
The technologies mentioned above used to exist as separate programs and in 2018 were combined to create Apple Business Manager as one consolidated service.
Here is an example of the portal view:
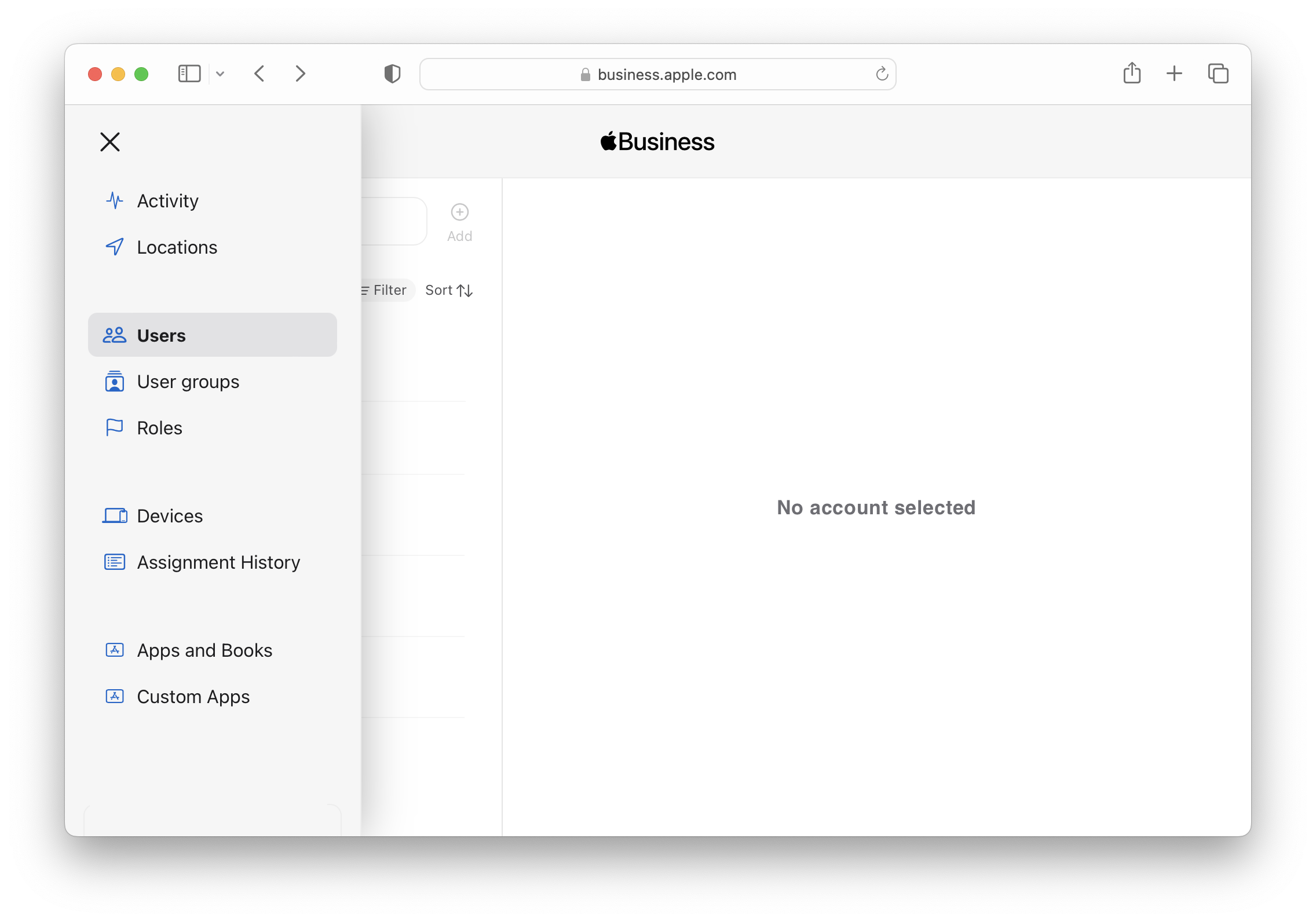
For more information about ABM please visit:
Apple School Manager (ASM)
Apple School Manager (ASM) is a version of Apple Business Manager specifically adapted for educational institutions.
In addition to features already available in ABM, ASM also allows school IT administrators to manage classes (for Classroom and Schoolwork) and shared iPads, and is integrated with student information systems (SIS) for quickly creating student and staff accounts and for easily deploying class related content.
Purchases made through ASM are entitled to Apple's educational discounts.
For more information about ASM please visit:
Apple Business Essentials (ABE)
Apple Business Essentials (ABE) is an entry-level mobile device management (MDM) service from Apple which enables organizations to configure and manage their user mobile devices.
ABE provides basic MDM functionality such as users onboarding, configuration management, application management, and restrictions.
In addition, ABE differs from traditional MDM offerings in that the plan also includes iCloud space for device backups, and integration with AppleCare+ for device repairs.
For more information visit the Apple Business Essentials product page.
Automated Device Enrollment (ADE)
Automated Device Enrollment (ADE, formerly Device Enrollment Program – DEP) is a technology designed to help businesses easily deploy and configure Apple devices. It automates out-of-the-box supervision and enrollment in MDM and simplifies the initial configuration of devices handed out to users.
The technology is available as part of ABM and ASM, and applies for devices that are added to these portals. Using ADE, devices automatically acquire supervision and MDM enrollment during setup after they have been connected to internet for the first time.
This saves IT departments the need to have devices shipped to them for initial setup before distribution to users. It also ensures that company-owned devices remain locked into MDM for ongoing management, even after they are restored to factory settings.
For more information about ADE please visit:
- Automated Device Enrollment and MDM
- Use Automated Device Enrollment
- Automated Device Enrollment MDM payload list
Supervision
As described in Organization / Supervising Identity / Supervising Host Certificate, supervision expresses a company or institution's ownership of a device. This ownership is enforced by a digital certificate, the supervision identity.
Once a device is supervised, the supervising organization is granted far greater control over it: new restrictions on the device's behavior become available, end-users passcode/password can be reset, device can be erased and in general user consent is no longer necessary to push configurations. Consequently, supervision should only be used on company owned devices and never in a BYOD context.
The process of supervising a device is generally part of device enrollment. Applying supervision can be done locally with Apple Configurator or iMazing Configurator for iOS, iPadOS, and tvOS devices, or remotely using Automated Device Enrollment for the same type of devices as well as for macOS ones in addition.
For more information please visit the Supervision section of our Understanding Supervision, MDM, ADE (DEP), and Volume Purchase (VPP) guide.
Apps and Books
Apps and Books (sometimes known as Volume Purchase, formerly Volume Purchase Program – VPP) is a section of the ABM and ASM portals which allows organizations and schools to purchase applications and digital books licenses in bulk, to be deployed and managed silently on devices through MDM, Apple Configurator, or iMazing Configurator.
Thousands of volume-purchasing-enabled applications are available from the App Store or Mac App Store in a wide range of categories. A selection of books from the Apple Books Store is also available for purchase through the section.
Custom applications developed to meet your organization’s specific business needs can also be purchased. Once authorized, they can be deployed in bulk similarly. More information about these is available on Apple's Learn about Custom Apps in Apple Business Manager page.
Volume Purchase allows organizations to use several payment methods. It also provides license portability between organization users and devices as well as centralized billing.
For more information on Volume Purchase visit Apple's Intro to purchasing content in Apple Business Manager.
Apple Developer Program
The Apple Developer Program is a comprehensive membership program designed to provide resources, tools and support for developers and organizations to create, test and distribute applications for Apple's platforms, including iOS, iPadOS, macOS, watchOS and tvOS.
The program grants access to beta software, developer forums, technical support and the ability to submit apps to the App Store for distribution to end users.
In addition, the program also provides access to features such as Apple Pay, Game Center and In-App Purchases that can be used to monetize the developed apps.
The program is available at different levels such as individual and organizational, with each level offering different capabilities and benefits to members. A similar program called the Apple Enterprise Developer Program offers even more capabilities specifically needed by enterprise developers.
For more information please head over to the Apple Developer Program page.
Apple Enterprise Developer Program
The Apple Enterprise Developer Program is a specialized membership program designed for businesses and organizations to develop, test and distribute proprietary iOS, iPadOS, macOS, watchOS and tvOS applications to their internal employees.
The program grants access to beta software, developer forums, technical support and the ability to distribute apps via a mobile device management (MDM) system, outside of the App Store.
This program is offered exclusively for organizations and is designed to meet the needs of large companies and organizations that require the development and distribution of internal proprietary applications to their employees. A similar program called the Apple Developer Program is available for all other developers.
For more information please head over to the Apple Enterprise Developer Program page.
Custom Enterprise App (In-House)
Custom enterprise apps, also known as in-house apps, are proprietary software applications developed and distributed specifically for use by a particular organization or business.
They are not available on the public app store, but are intended for internal use by employees, members or partners of the organization.
These apps are designed to meet the specific needs of the organization, improve work efficiency, automate internal processes, or provide specialized functionality not available in standard apps. Common examples of internal applications are internal HR tools, inventory management systems, or company-specific communication platforms.
Specially designed for macOS, iOS or iPadOS and to allow organizations to create apps that can be installed on these OSs without passing App Review (which is a requirement for any other type of apps).
These applications are deployed through a mobile device management (MDM) solution and are only accessible to members of the organization, ensuring data security and privacy.
Configuration Profile (.mobileconfig)
Apple Configuration profiles are small data files that are used to apply certain configurations to macOS iOS, iPadOS and tvOS devices. They can contain various settings, restrictions, certificates, and other content that enable or disable functionality on the device.
The profiles allow a device owner to load sets of predefined settings to their device with minimal or no interaction at all, instead of having to enter the settings manually on the device itself. They include some of the most common settings found in the Settings app on the device. Among them are settings to configure Wi-Fi networks, email accounts, desired passcode behavior, pop notifications, VPNs and more.
Configuration profiles can also include settings that are not available through the Settings app, such as what certificates should be provided on the device, what web clips should the device show on the home screen, and they can also for instance install custom fonts on the device.
Furthermore, through configuration profiles a device owner can set certain restrictions on the device such as disabling the cameras, turning off iCloud or other Apple services, forcing encryption and passcode, and more.
Organizations that manage hundreds of devices or more, typically use configuration profiles to load all of their necessary organizational settings into a certain device in one go, and to place restrictions according to their compliance and data protection policy.
Configuration profiles can be encrypted in order to protect sensitive settings, and can be digitally signed to authenticate their issuer.
Apple Configuration Profiles can be created and edited with iMazing Profile Editor.
For more information please read our Configuration Profiles guide.
Provisioning Profile (.mobileprovision)
Provisioning profiles are used to distribute apps. It enables macOS, iOS, iPadOS, and tvOS devices to run applications that were developed by the owner of a profile, without having to download the app from the App Store.
They are typically used by app developers during the development process to load apps into development or test devices, which will otherwise not run apps not digitally-signed by Apple.
Provisioning profiles are issued by Apple for developers on a per-device basis. This means that a single provisioning profile is good only for the device it was issued for.
For more information please read Apple's documentation:
- Create a development provisioning profile
- Create an ad hoc provisioning profile (iOS, tvOS, watchOS)
Managed Apple Accounts
A managed Apple Account is a specially created and controlled Apple account that is assigned to employees, students or members of an organization, for use in place of personal Apple Accounts. These accounts are managed by an administrator with ABM or ASM and provide access to Apple services such as iCloud Drive, Contacts, Calendars, etc. However, unlike with traditional Apple Accounts, they cannot make content purchases on the App Store, on the iTunes Store, or on Apple Books.
Administrators have the ability to set specific access permissions and restrictions on the use of these accounts. This allows organizations to enforce their policies and compliance requirements. In addition, they can also configure managed accounts for federated authentication which allows streamlined access to different resources in the organization.
For more information please read Apple's documentation:
Apple Account (standard)
An Apple Account is an user account that you can use to access various Apple services and products, such as the App Store, iCloud, iTunes, Apple Music, Apple TV, etc.
Your Apple Account is a personal account that allows you to log in to all these different services using the same username and password.
When you create an Apple Account, you'll be asked to provide some personal information, such as your name, email address, and a password.
Managed Apple Accounts are different in that they are managed by an organization.
For more information about Apple Account, please visit Apple Account Support page.
User Enrollment (BYOD)
User enrollment is designed for BYOD - or bring-your-own-device - deployments. This means that the user, not the organization, owns the device.
User enrollment requires managed Apple Accounts. These are owned and managed by an organization and allow employees to access certain Apple services.
User Enrollment is integrated with Managed Apple Accounts to establish a user identity on the device. However, the Managed Apple Account can be used in conjunction with the personal Apple Account that the user has already signed in with: the two do not interact with each other.
There are two main ways for users to enroll a personal device in User Registration:
- User enrollment through an account
- User enrollment by installing manually an MDM enrollment configuration profile
Once the user registration is complete, a separate volume is automatically created on the device. This volume contains the software related to the professional use of the device.
Follow this link for more information about User Enrollment methods.
Device Enrollment
Device Enrollment allows an organization to enforce its ownership on a device. It means the enrollment is applied at the device level rather than at the user one. The device is enrolled to an MDM or a local management tool solution before the user receives the device.
Device Enrollment usually implies supervising the device with a supervising identity to enforce the organization ownership.
Device enrollment allows applying a broader set of configuration profile payloads and settings to a device. For situations where the user has left the organization or forgot their passcode/password, the supervising identity allows for resetting it as well as for erasing the device.
Device enrollment can be done locally with Apple Configurator or iMazing Configurator, or remotely using Automated Device Enrollment.
Follow this link for more information about Device Enrollment.
Organization / Supervising Identity / Supervising Host Certificate
In the context of mobile device management an Organization (also known as the Supervision Identity or the Supervising Host Certificate), is a digital certificate containing metadata about the owning organization (name, department, address, etc...). The certificate is used during supervision to establish a privileged link between iOS/iPadOS devices and their supervising host, and later to allow the host to make any privileged modifications to the device.
When supervising locally, a host is typically a computer running iMazing Configurator or Apple Configurator. In this scenario the applications used to manage supervision allow users to generate organizations and save them to the computer certificate store (Keychain on macOS and Certificate Store on Windows). When supervising using Automated Device Enrollment via ABM or ASM, the host is typically the MDM server assigned to the supervised device, and the certificate is stored by that server.
Since the certificate is required to make privileged changes to supervised devices, some MDM vendors allow exporting MDM-generated certificates and importing externally-generated ones.
For more information please read our Organization & Supervision guide.
Blueprint
A blueprint in the context of device management is a template containing a set of configurations and actions. MDM solutions or tools such as Apple Configurator or iMazing Configurator can apply blueprints to multiple devices to prepare and configure them. A blueprint can contain a list of configuration profiles, a list of apps that need to be installed and some actions such as erasing the device, updating the OS, supervising the device with a supervising identity, restoring a backup, etc.
Certificate
A certificate is an electronic document that contains information about an entity, such as a person or organization, and is often issued by a trusted third party called a certificate authority (CA). Certificates can be used for encrypting and signing data, authenticating users and devices, and establishing trust between different parties.
In Apple's mobile device management (MDM) context, certificates are used to establish trust and secure communication between the MDM server and the managed devices. They are used to ensure that only authorized devices can communicate with the server and to authenticate users and secure data on the devices.
For importing and exporting supervising identities, Apple uses the PKCS #12 file format, which is specifically designed to store a private key and its associated certificate(s) securely in one file. It is protected by a password or passphrase and can also be used to store multiple private keys and certificates.
The file format is binary and the file extension is usually .p12 or .pfx. From a historical point of view, the PKCS #12 format is a successor to the PFX format used by Microsoft. However, the terms PKCS #12 and PFX are sometimes used interchangeably. This format is widely supported by many different applications and platforms including Windows and macOS.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a collection of tools and processes used to establish a secure method of exchanging digital information over the internet. At the heart of PKI is the use of a pair of cryptographic keys, one public and one private, to encrypt and decrypt data. This allows for secure communication without the need for a shared secret key.
PKI also includes the use of a trusted third party, known as a certificate authority (CA), which is responsible for issuing digital certificates. These certificates are used to confirm the identity of the certificate holder, as well as to link a public key with the identity of an individual, organization, or device.
PKI is widely used in various applications, such as secure email, online transactions, virtual private networks, digital signatures, and more.
Apple's PKI page lists many of the company's root and intermediate certificates, as those are required in order to establish trust in documents, websites, and files signed with certificates that the company issues.
Device Management / Remote Management
Device Management or Remote Management (for old OS versions) in the context of Apple mobile device management (MDM) and ABM or ASM refers to the ability to remotely configure and control a fleet of Apple devices, including iPhones, iPads, and Macs, using an MDM server.
IT administrators can use the server to manage the devices by enrolling them, configuring settings, and installing apps. They can also use the server to monitor the devices, including their location, battery level, and compliance with security policies.
Additionally, Device Management allows IT administrators to remotely wipe or lock a device if it is lost or stolen, or if it is not in compliance with security policies, to protect company data and ensure compliance with company policies.
Overall, Device Management feature allows IT administrators to have a central control over organizations' Apple devices and ensure data security and compliance with company policies.
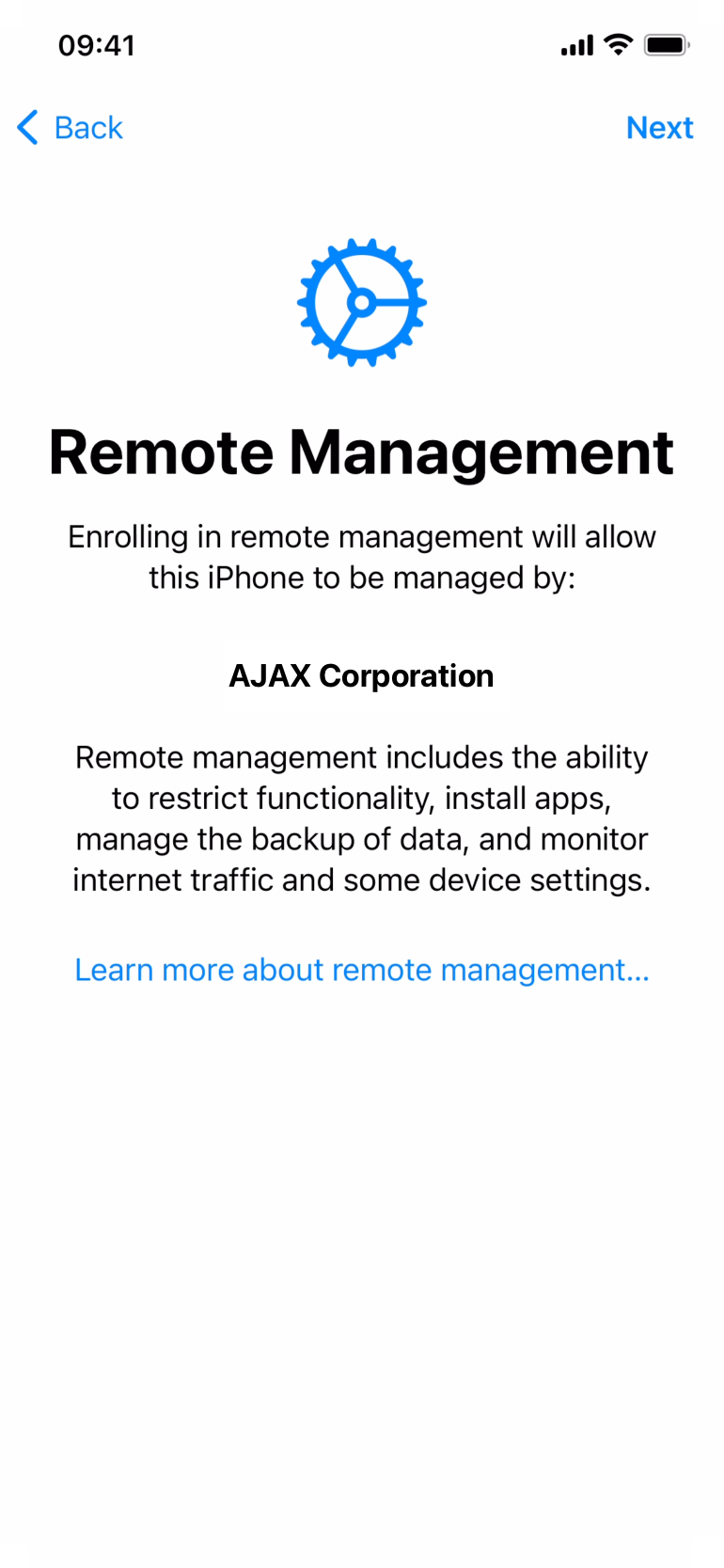
You can easily see this when you receive a device pre-configured by ABM/ASM and an MDM, when the Device Management or Remote Management (for old OS versions) screen appears during setup and displays the name of the organization that manages it:
Volume Purchase
Volume Purchase is the ability for organizations to purchase applications and digital books from Apple in bulk from the ABM or ASM portals, where it can be found under the section named Apps and Books.
For more information about Volume Purchase, please visit About Volume Purchase in the App Store on Mac page.
Volume Purchase Program (VPP) (legacy)
Volume Purchase Program (VPP) was originally an independent platform that was later merged into ABM and ASM, and is today known as Volume Purchase, available in the Apps and Books section of ABM and ASM.
Device Enrollment Program (DEP) (legacy)
Device Enrollment Program (DEP) was originally an independent program that was later merged into ABM and ASM, and is today known as Automated Device Enrollment.
Student Information System (SIS)
A student information system (SIS) is a software solution that allows educational institutions to digitize and therefore manage student information more efficiently.
It is a system that allows educational institutions to make all student information, such as course materials and class schedules, available online.
For more information about SIS in Apple device management context, please visit Apple's Student Information System page.
macOS Server (legacy)
macOS Server, also known as Mac OS X Server (first version was named 10.1 Puma Server) and later OS X Server, was provided as the server operating system for the Xserve rack-mounted server computers designed by Apple. It was also optionally preinstalled on the Mac Mini and Mac Pro. It used to also be sold separately for use on any Macintosh computer that met the minimum system requirements.
Starting with Mac OS X 10.7 Lion, macOS Server was offered as an add-on package, distributed through the Mac App Store and installable over the conventional Mac operating system.
In April 2022, Apple announced that it had discontinued macOS Server and that the most popular features (caching server, file sharing server, and Time Machine server) were already included in every copy of macOS High Sierra (or later versions), so users could still access them.
The macOS server allowed the use of different Apple services such as Profile Manager, Open Directory or Xsan. It also allowed a Mac to take on several of the popular server roles such as Firewall, VPN, Radius, DHCP, DNS, etc.
Current macOS Server customers today can still download and use the application with macOS up to and including Monterey.
For more information about this - legacy - Server OS, please visit Apple's About macOS Server 5.7.1 and later article.
Preference File Manifest (PFM)
In the context of Apple mobile device management, a Preference File Manifest (PFM) is an XML document (in Plist format) containing keys of various types (strings, boolean, numbers, arrays etc.) to describe a set of configuration that can help in generating Apple configuration profiles or default application settings.
Manifests are used by applications such as iMazing Profile Editor for displaying the available preferences for various Apple configuration domains and application settings that users are interested in managing.
Manifest files are ideally created by app developers for facilitating their apps configurations, to describe all available configurable settings. When official manifests are not available, the system administrator community creates custom ones. A great community project is the ProfileManifests GitHub repository.
For more information about the Preference Manifest format, please visit Apple's Preference Manifests Files for Managed Clients Overview page.
Property list files (.plist)
Property list files contain serialized objects (dictionary of various types of key/value) used on Apple operating systems. Those files use the .plist file name extension.
Property list files are often used to store a user's settings. They are also used to store information about packages and applications.
For more information about .plist format, please visit Wikipedia's Property list Article page.
Trust Anchor Certificate
In the Apple mobile device management architecture, the trust anchor certificate is used to confirm the trust relationship between the device and the MDM server during enrollment phase. This is similar to a certificate trust chain, containing the root certificate and the intermediary ones.
For more information about digital certificates in Apple device management context, please visit Apple's Understanding Digital Certificates Guide page.
Multi Factor Authentication (MFA or 2FA for two-factor authentication)
Multi-factor authentication is a method of electronic authentication whereby a user can only access a system or an application after successfully presenting at least two pieces of evidence (or factors) to an authentication mechanism:
- The account password
- A code received on a trusted device
- Other optional factors can be: biometric, geolocation, etc.
MFA protects the user from access by an unauthorized third party who may have discovered, for example, a login password.
Nowadays, Google Authenticator and Microsoft Authenticator are the most widely used third-party applications, as well as receiving a SMS as a second authentication factor.
Receiving a code by SMS, on a trusted Apple device or by generating it with an authenticator_ app, after entering an account password, is called 2FA because there is two factors of authentication involved.
For more information about this electronic authentication method, please visit the wikipedia article on Multi-factor authentication.
Apple Deployment Programs (ADP) (legacy)
Until november 2022 this programs provided organizations with tools and resources to streamline the deployment of iOS, iPadOS and macOS devices, including device provisioning and configuration, app distribution, etc.
These programs included DEP (Device Enrollment Program now known as Automated Device Enrollment) and VPP (Volume Purchase Program).
They are now available in the following two platforms:
- For education customers: Apple School Manager
- For business customers: Apple Business Manager (or Apple Business Essentials)
Please note that is a legacy program and it is now required to Upgrade from Apple Deployment Programs and the Volume Purchase Program.
Apple Push Notification Service (APNs)
Apple Push Notification Service (APNs) is a service provided by Apple that allows third-party app developers to send notifications from their server to iOS, iPadOS and macOS devices. APNs allows developers to push notifications, such as alerts, badges and sounds, to their users, even when the app is not running in foreground.
For example, when a server wants to send a notification to a user's device, it sends the notification to Apple APNs servers, which then forward it to the device.
APNs is responsible for managing the delivery of notifications to devices, including routing notifications to the correct device, maintaining a persistent connection to the device, and ensuring secure delivery.
In the context of Mobile Device Management, APNs plays a key role in enabling MDM solutions to communicate with iOS, iPadOS, and macOS devices.
MDM solutions use APNs to send notifications to managed devices to let them know that the MDM server has a command payload that needs to be retrieved by the device.
MDM commands allow for instance an admin to remotely configure, wipe, lock or unlock a device.
For more information about this notification service, please visit the wikipedia article on Apple Push Notification service.
App Redemption Code
An app redemption code is a unique code generated by the Apple App Store that allows a customer to download and install a specific app or in-app purchase.
They can be purchased by organizations and educational institutions through the Apple Apps and Books program.
Redemption codes can be redeemed by end users via the App Store app on their iOS, iPadOS or macOS devices.
Once a redemption code has been redeemed, the app or in-app purchase is added to the user's Apple Account account, which can then be downloaded and installed on their device.
Redemption codes can be used for a variety of purposes, including distributing apps and books to users, or providing access to specific features.
For more information about App Redemption Code and Gift Card, please visit Apple's Support page.
D-U-N-S Number (Data Universal Numbering System)
A D-U-N-S number is a unique, nine-digit identifier assigned by Dun & Bradstreet (also know as D&B), an international provider of business credit information and risk management solutions. D-U-N-S stands for Data Universal Numbering System.
The D-U-N-S number is used as a standard identifier for businesses around the world and is widely recognized and accepted by many organizations, including governments, lenders, and suppliers.
Obtaining a D-U-N-S number is a straightforward process. Businesses can apply for a D-U-N-S number through the D&B website.
D&B will verify the information provided by the business, including its legal name, address, and ownership structure, and will assign a D-U-N-S number if the information is found to be accurate.
For more information about Data Universal Numbering System, please visit Dun & Bradstreet's website.
Volume Purchase Token (VPP Token or sToken)
The Apple Volume Purchase Token is a type of token used in Apple's Volume Purchase Program by MDM solutions, iMazing Configurator or Apple Configurator to manage licenses purchased via the Apps & Books section of ABM or ASM.
It can be found in the Preferences section of an account having the appropriate role on the ABM/ASM portal.
For more information about Volume Purchase Token (VPP Token or sToken), please visit Manage server tokens in Apple Business Manager.
Managed Apps
Managed Apps refer to apps that are managed and controlled by an organization or institution through mobile device management (MDM) solutions.
A MDM solution can install apps to iOS, iPadOS or macOS devices and manage their configuration.
Managed Apps can be configured to enforce security policies, such as requiring a password to access the app, or to restrict the use of certain features.
For example, a managed book app can be used to distribute educational material or a managed productivity app can be used to distribute work-related content.
For more information about Managed Apps, please visit Distribute Managed Apps to Apple devices guide.
Managed Books
Managed Books refers to the ability for admins to distribute books to specific users or groups of users within their organization, from a MDM solution.
For more information about Managed Books, please visit Content distribution methods for Apple devices.
Single App Mode
Single app mode (also known as kiosk mode) locks your organization's iPhone, iPad or iPod touch devices to display a single app. This is a very powerful feature of iOS that allows Apple's mobile devices to be used as single-use digital tools in your business or institution.
Please note that Single App Mode requires the device to be supervised.
iMazing Configurator allows you to manage this feature through a blueprint. It can also be managed directly from a MDM solution.
For more information about the Single App Mode, please visit our iMazing Configurator documentation here:
- Put iPhone, iPad and iPod touch in Single App Mode (Kiosk Mode)
- Put Multiple Apple Devices in Single App Mode with iMazing Configurator
Mobile Application Management (MAM)
Mobile Application Management (MAM) describes the software and services responsible for provisioning and controlling access to mobile applications used in business settings on enterprise-provided mobile operating systems and on Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) systems.
Mobile application management provides granular application-level controls that allow system administrators to manage and secure application data.
MAM differs from Mobile Device Management (MDM), which focuses on device-wide control, and requires users to enroll or register their device to a server.
MDM solutions intrinsically include MAM features. Have a look to Managed Apps for more details.
For more information about MAM, please visit the wikipedia article on Mobile Application Management.

